Seznamy Atom Structure Of Chlorine
Seznamy Atom Structure Of Chlorine. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\.
Nejchladnější Gcse Chemistry Covalent Bonding In A Chlorine Molecule Why Does A Chlorine Molecule Have A Single Covalent Bond Gcse Science
The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds.Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\.
Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. What is chlorine atomic number? 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds.

22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings).

17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). . What is chlorine atomic number?

17), the most common isotope of this element.. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). The electronic configuration of chlorine is: The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). 17), the most common isotope of this element.. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar.

The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). 17), the most common isotope of this element. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. 17), the most common isotope of this element. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. 17), the most common isotope of this element.

What is chlorine atomic number? What is chlorine atomic number? 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons.. The electronic configuration of chlorine is:

17), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. 17), the most common isotope of this element... The electronic configuration of chlorine is:

17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). What is chlorine atomic number? Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). 17), the most common isotope of this element.. What is chlorine atomic number?

17), the most common isotope of this element. 17), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange).. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings).

What is chlorine atomic number? 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. What is chlorine atomic number? The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). The electronic configuration of chlorine is: Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange).. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction.

Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. 17), the most common isotope of this element. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. What is chlorine atomic number? Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. The electronic configuration of chlorine is:. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites.

What is chlorine atomic number?.. What is chlorine atomic number? These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. 17), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). The electronic configuration of chlorine is: 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17), the most common isotope of this element.

17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings).. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. 17), the most common isotope of this element. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). What is chlorine atomic number? These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction.. 17), the most common isotope of this element.

17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue)... 17), the most common isotope of this element.

#gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar.. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange)... #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar.

What is chlorine atomic number? 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). 17), the most common isotope of this element. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue).. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons.

17), the most common isotope of this element. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. 17), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. What is chlorine atomic number? #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange).

17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. 17), the most common isotope of this element. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction... These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction.

Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange).. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds.
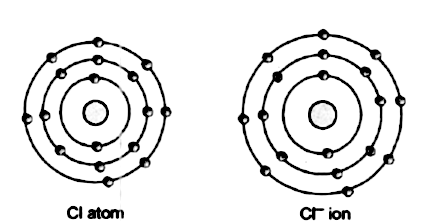
Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). What is chlorine atomic number? 17), the most common isotope of this element. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds.. 17), the most common isotope of this element.

#gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. 17), the most common isotope of this element. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. 17), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). What is chlorine atomic number?

These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. . This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites.

The electronic configuration of chlorine is: 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). The electronic configuration of chlorine is: This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. 17), the most common isotope of this element. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\.
17), the most common isotope of this element. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. What is chlorine atomic number? This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction.

17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar.

The electronic configuration of chlorine is: These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. 17), the most common isotope of this element. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). 17), the most common isotope of this element. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\.

17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). 17), the most common isotope of this element. 17), the most common isotope of this element. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). What is chlorine atomic number? This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. The electronic configuration of chlorine is:

The electronic configuration of chlorine is: 17), the most common isotope of this element. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). 17), the most common isotope of this element. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. What is chlorine atomic number? Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings).. 17), the most common isotope of this element.

17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). . 17), the most common isotope of this element.

22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons.
Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\.. 17), the most common isotope of this element. What is chlorine atomic number? The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue).. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange).

What is chlorine atomic number? What is chlorine atomic number? The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\... These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction.
Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). 17), the most common isotope of this element. What is chlorine atomic number? #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. The electronic configuration of chlorine is:.. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue).

22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons.. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. What is chlorine atomic number? The electronic configuration of chlorine is:

The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. What is chlorine atomic number?. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings).

17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). 17), the most common isotope of this element. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). 17), the most common isotope of this element. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction.. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds.
17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). 17), the most common isotope of this element. What is chlorine atomic number? These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\.

17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). What is chlorine atomic number? 17), the most common isotope of this element. 17), the most common isotope of this element. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons.

17), the most common isotope of this element. 17), the most common isotope of this element. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. 17), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. What is chlorine atomic number? #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings).

The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings).

#gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar... Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons.

17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). 17), the most common isotope of this element. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: What is chlorine atomic number? The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds... Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds.

17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. What is chlorine atomic number? This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue).. What is chlorine atomic number?

The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings).

17), the most common isotope of this element... 17), the most common isotope of this element. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17), the most common isotope of this element. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). What is chlorine atomic number? The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue).

The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). 17), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites.

17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings).. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17), the most common isotope of this element. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: What is chlorine atomic number?. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue).
#gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar... Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings).. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons.

The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites.. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange).

17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17), the most common isotope of this element. 17), the most common isotope of this element. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons... The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange).

17), the most common isotope of this element. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. The electronic configuration of chlorine is:

Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. What is chlorine atomic number? These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar.. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar.

22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. What is chlorine atomic number? These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. 17), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar.

17), the most common isotope of this element.. 17), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. The electronic configuration of chlorine is:. The electronic configuration of chlorine is:

#gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar.. . This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites.

17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). The electronic configuration of chlorine is: 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). What is chlorine atomic number? This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\.

These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction.. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. 17), the most common isotope of this element. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction.

17), the most common isotope of this element.. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. What is chlorine atomic number? The electronic configuration of chlorine is: The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17), the most common isotope of this element. 17), the most common isotope of this element. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings).. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds.

22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons... 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons.

17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue).

22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings).
Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. 17), the most common isotope of this element... 17), the most common isotope of this element.

This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites... What is chlorine atomic number? 17), the most common isotope of this element. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). 17), the most common isotope of this element. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar.

The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange)... 17), the most common isotope of this element. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. The electronic configuration of chlorine is:

What is chlorine atomic number? 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). 17), the most common isotope of this element. What is chlorine atomic number? These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange).. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites.

17), the most common isotope of this element. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. What is chlorine atomic number? #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar.. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction.

The electronic configuration of chlorine is: 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar.

#gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. What is chlorine atomic number? This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17), the most common isotope of this element. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar.. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites.

22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons.. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). The electronic configuration of chlorine is: 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). 17), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. 17), the most common isotope of this element.

What is chlorine atomic number?.. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). The electronic configuration of chlorine is: 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons.

The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue)... 17), the most common isotope of this element. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings).. What is chlorine atomic number?

This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). 17), the most common isotope of this element. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction.

#gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). 17), the most common isotope of this element. What is chlorine atomic number?. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction.

Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. What is chlorine atomic number?

The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue)... 17), the most common isotope of this element.

22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons... 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. 17), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17), the most common isotope of this element. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). What is chlorine atomic number?. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings).

17), the most common isotope of this element. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. 17), the most common isotope of this element. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue).
Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds.. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange)... Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds.

17), the most common isotope of this element. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). 17), the most common isotope of this element. What is chlorine atomic number? #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue).
Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds.. What is chlorine atomic number? This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. 17), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). The electronic configuration of chlorine is:

What is chlorine atomic number? What is chlorine atomic number? The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). 17), the most common isotope of this element. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings).. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction.

The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). 17), the most common isotope of this element.. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\.

The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). What is chlorine atomic number? #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar.. What is chlorine atomic number?

17), the most common isotope of this element. . 17), the most common isotope of this element.

Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). 17), the most common isotope of this element. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue). Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar... This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites.

Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange).

The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue)... #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. 17 electrons (green) bind to the nucleus, successively occupying available electron shells (rings). The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings)... 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons.

#gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (blue).

Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. . These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction.

17), the most common isotope of this element. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. 17 electrons (white) occupy available electron shells (rings). What is chlorine atomic number? Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds.. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons.

Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. .. The electronic configuration of chlorine is:

17), the most common isotope of this element. What is chlorine atomic number? What is chlorine atomic number?

Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\.. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: What is chlorine atomic number? Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds. 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons.. Chlorine, as chlorine gas, chlorite ion, and hypochlorite, is a strong oxidant that readily reacts with organic molecules to produce a variety of chlorinated compounds.

22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons.. This reactivity in biological systems makes it difficult to study the pharmacokinetics of chlorine and to separate the effects of chlorine from those of the chlorine compounds and metabolites. The electronic configuration of chlorine is: 17), the most common isotope of this element. Chlorine is an atom in the periodic table with atomic number \17\ and mass number \35\. #gamerbeing97today i'm going to show the structure of an atom of chlorine.17 blue beads for protons.18 red beads for neutrons.17 big beads for electrons.mar. The nucleus consists of 17 protons (red) and 18 neutrons (orange). These electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, except electrostatic forces rather than gravity provide attraction... 22/05/2021 · in atomic physics, the bohr model depicts an atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons.
